Which of the following is true of lysosomes? These enigmatic organelles, often referred to as the cell’s “digestive system,” play a crucial role in maintaining cellular health and orchestrating a symphony of vital processes within the intricate realm of the cell.
Embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries of lysosomes, uncovering their unique characteristics, functions, and therapeutic applications.
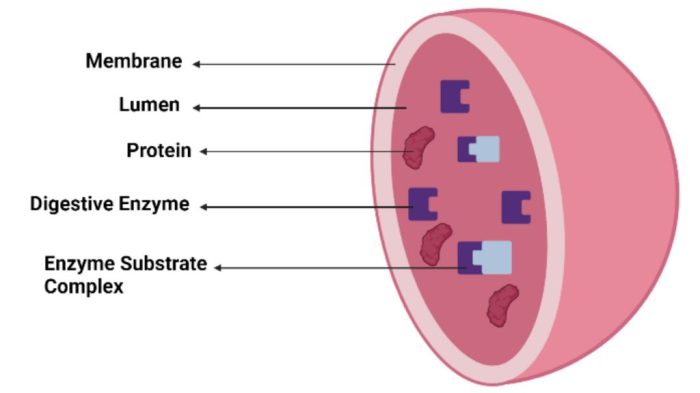
Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles found in eukaryotic cells, equipped with an arsenal of hydrolytic enzymes capable of degrading various biomolecules. They serve as the primary site for intracellular digestion, engulfing foreign particles, damaged organelles, and cellular debris. Moreover, lysosomes participate in autophagy, a process of self-digestion that eliminates damaged cellular components, ensuring cellular renewal and homeostasis.
1. Characteristics of Lysosomes

Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. They are characterized by their acidic internal pH, which is maintained by a proton pump in the lysosomal membrane. Lysosomes contain a variety of hydrolytic enzymes capable of degrading various biomolecules, including proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids.
Lysosomes play a crucial role in cellular homeostasis by digesting and recycling cellular waste products, damaged organelles, and foreign particles. They also participate in autophagy, a process by which cells break down and recycle their own components.
Functions of Lysosomes
- Digestion of cellular waste products and damaged organelles
- Recycling of cellular components through autophagy
- Defense against pathogens and immune surveillance
- Targeted drug delivery and enzyme replacement therapies
2. Lysosomal Enzymes and Their Functions

Lysosomes contain a wide range of hydrolytic enzymes, each with a specific function in the degradation of various biomolecules.
Types of Lysosomal Enzymes
- Proteases: Degrade proteins
- Nucleases: Degrade nucleic acids
- Lipases: Degrade lipids
- Glycosidases: Degrade carbohydrates
- Phospholipases: Degrade phospholipids
The activity of lysosomal enzymes is tightly regulated to prevent damage to the cell. Enzymes are synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus and then transported to lysosomes, where they are activated by the acidic pH.
3. Lysosomal Storage Disorders: Which Of The Following Is True Of Lysosomes
Lysosomal storage disorders are a group of inherited metabolic diseases caused by defects in lysosomal enzymes. These defects result in the accumulation of undigested substrates within lysosomes, leading to cellular dysfunction and tissue damage.
Examples of Lysosomal Storage Disorders
- Gaucher disease: Deficiency of glucocerebrosidase
- Fabry disease: Deficiency of alpha-galactosidase A
- Pompe disease: Deficiency of acid alpha-glucosidase
- Tay-Sachs disease: Deficiency of hexosaminidase A
Clinical manifestations of lysosomal storage disorders vary depending on the specific enzyme deficiency. Common symptoms include neurological impairment, skeletal abnormalities, and organ dysfunction.
4. Role of Lysosomes in Autophagy
Autophagy is a process by which cells break down and recycle their own components. Lysosomes play a central role in autophagy by providing the acidic environment and hydrolytic enzymes necessary for the degradation of cellular debris.
Involvement of Lysosomes in Autophagy
- Sequestration of cellular components into autophagosomes
- Fusion of autophagosomes with lysosomes to form autolysosomes
- Degradation of cellular components within autolysosomes
- Recycling of degraded components back into the cell
Autophagy is essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis and preventing the accumulation of damaged proteins and organelles.
5. Lysosomes and Immune Function

Lysosomes play a crucial role in the immune system by facilitating the phagocytosis and digestion of foreign particles, such as bacteria and viruses.
Contribution of Lysosomes to Immune Function
- Phagocytosis of foreign particles by phagocytic cells
- Fusion of phagosomes with lysosomes to form phagolysosomes
- Degradation of foreign particles within phagolysosomes
- Presentation of antigens to immune cells
Lysosomal function is essential for the defense against pathogens and immune surveillance.
6. Therapeutic Applications of Lysosomes
Lysosomes have potential therapeutic applications in medicine, including targeted drug delivery and enzyme replacement therapies.
Targeted Drug Delivery, Which of the following is true of lysosomes
Lysosomes can be harnessed as carriers for targeted drug delivery. Drugs can be encapsulated within lysosomes and then delivered to specific cells or tissues, reducing systemic side effects.
Enzyme Replacement Therapies
Enzyme replacement therapies involve the administration of functional lysosomal enzymes to patients with lysosomal storage disorders. This treatment can help to alleviate the symptoms of the disease by restoring lysosomal function.
FAQ Insights
What are lysosomes primarily responsible for?
Lysosomes are responsible for intracellular digestion, breaking down biomolecules, foreign particles, and damaged organelles.
What is the role of lysosomes in autophagy?
Lysosomes play a crucial role in autophagy, a process of self-digestion that eliminates damaged cellular components, promoting cellular renewal.
How do lysosomes contribute to immune function?
Lysosomes aid in immune function by engulfing and digesting foreign particles, contributing to the body’s defense against pathogens.