Air masses and fronts review worksheet answer key – Air masses and fronts are fundamental components of atmospheric circulation, influencing weather patterns and shaping the climate of different regions. Understanding their characteristics and interactions is crucial for weather forecasting and comprehending global climate dynamics. This comprehensive review worksheet answer key provides an in-depth exploration of air masses, fronts, and their interactions, offering a valuable resource for students, meteorologists, and anyone seeking to enhance their knowledge of atmospheric processes.
Air Masses
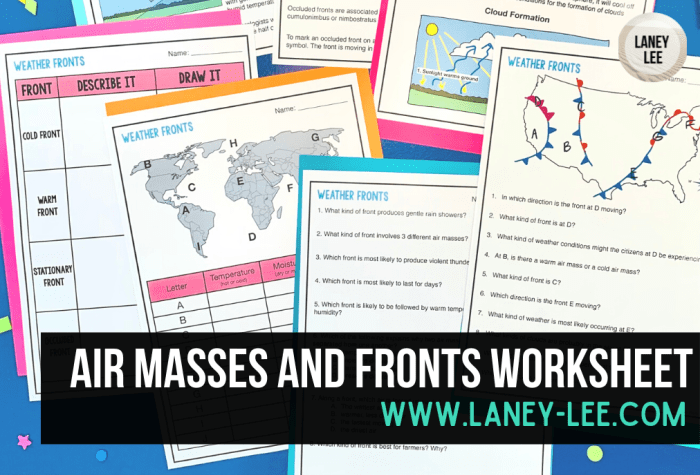
Air masses are large bodies of air that have similar temperature and humidity characteristics. They are classified according to their source region and their temperature and moisture content.
The four main types of air masses are:
- Continental polar (cP)air masses originate over high-latitude land areas and are cold and dry.
- Maritime polar (mP)air masses originate over high-latitude oceans and are cool and moist.
- Continental tropical (cT)air masses originate over low-latitude land areas and are warm and dry.
- Maritime tropical (mT)air masses originate over low-latitude oceans and are warm and moist.
The formation of air masses is influenced by several factors, including the temperature and moisture content of the surface over which they form, the length of time they remain over the surface, and the presence of any nearby mountain ranges or bodies of water.
Fronts

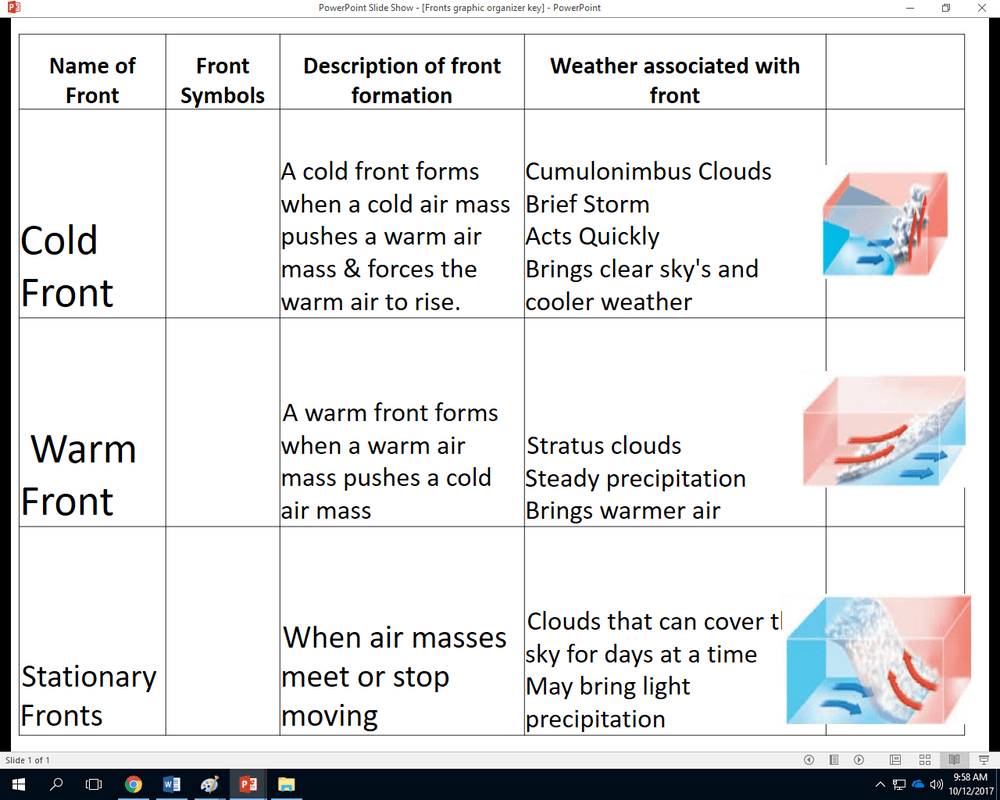
Fronts are boundaries between two air masses with different temperature and humidity characteristics. They are classified according to the type of air masses that they separate.
The four main types of fronts are:
- Cold frontsseparate cold air masses from warmer air masses.
- Warm frontsseparate warm air masses from colder air masses.
- Stationary frontsseparate two air masses that are not moving.
- Occluded frontsform when a cold front overtakes a warm front.
Fronts form when two air masses with different densities meet. The denser air mass will push under the less dense air mass, creating a front.
Air Mass and Front Interactions
Air masses interact with each other in a variety of ways. When two air masses with different temperatures meet, they can create a front. Fronts can also form when two air masses with different densities meet.
The weather associated with a front depends on the type of front. Cold fronts are typically associated with thunderstorms, while warm fronts are typically associated with rain or snow. Stationary fronts are typically associated with cloudy and drizzly weather.
Worksheet Answer Key: Air Masses And Fronts Review Worksheet Answer Key
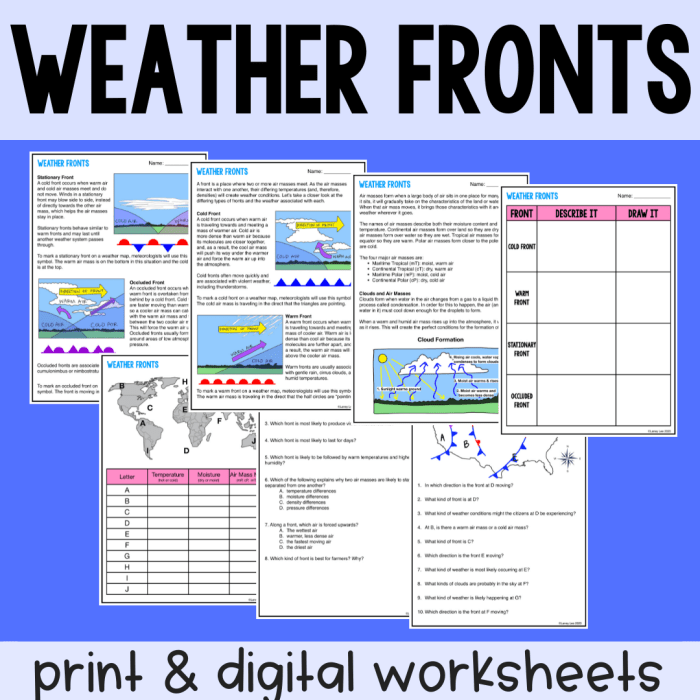
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What are air masses? | Air masses are large bodies of air that have similar temperature and humidity characteristics. |
| What are the four main types of air masses? | Continental polar (cP), maritime polar (mP), continental tropical (cT), and maritime tropical (mT). |
| What factors influence the formation of air masses? | The temperature and moisture content of the surface over which they form, the length of time they remain over the surface, and the presence of any nearby mountain ranges or bodies of water. |
| What are fronts? | Fronts are boundaries between two air masses with different temperature and humidity characteristics. |
| What are the four main types of fronts? | Cold fronts, warm fronts, stationary fronts, and occluded fronts. |
| How do fronts form? | Fronts form when two air masses with different densities meet. |
| What weather is associated with different types of fronts? | Cold fronts are typically associated with thunderstorms, warm fronts are typically associated with rain or snow, and stationary fronts are typically associated with cloudy and drizzly weather. |
FAQ Summary
What are the key characteristics of air masses?
Air masses are large bodies of air with relatively uniform temperature and humidity characteristics. They are classified based on their source region, which determines their thermal and moisture properties.
How do fronts form?
Fronts arise at the boundaries between air masses with contrasting temperatures and densities. As these air masses collide, they create a zone of transition characterized by distinct weather patterns.
What are the different types of fronts?
There are several types of fronts, including cold fronts, warm fronts, stationary fronts, and occluded fronts. Each type is associated with specific weather conditions and can have significant impacts on local weather patterns.